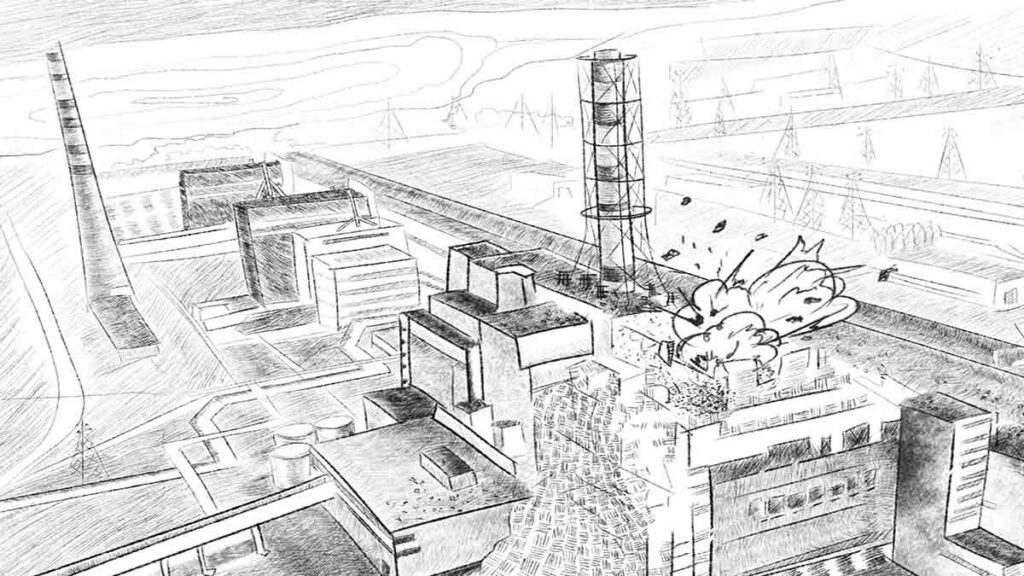
The tragedy at the Chernobyl nuclear power station is the largest man-made and humanitarian disaster of the last century. Experts from all over the world continue to eliminate its environmental consequences so far. Lessons, conclusions and reasons, are extremely important for the history of the world nuclear energy and the development of peaceful atom. Therefore, today, after 33 years, this topic has not lost its relevance.
The accident happened on April 26, 1986. An explosion, resulting in more than 200 thousand square kilometers were exposed to radioactive contamination, has occurred in the fourth power unit, located 120 km from Kiev – the capital of Ukraine. The Chernobyl disaster led to particularly serious consequences in the territory of Belarus which was a closely neighbourhood. Radioactive contamination partially reached Norway, Finland and Sweden. According to the expert reports, the maximum contamination by radiation decay products affected the territories of Ukraine, Belarus and Russia.
The exact number of disaster victims has not been announced yet. The approximate data is about 4 thousand people who died from the radiation exposure immediately at the time of the tragedy. According to Greenpeace, the total number of the dead and the injured can vary from 90 thousand to 350 thousand people.
There is no single and unconditional version, as they say, regarding the causes of the Chernobyl environmental disaster. Most experts are inclined to a fateful combination of circumstances in the form of technical errors of personnel and imperfections in the design of the reactor. The USSR leadership took measures to classify data on its real and predicted consequences. Some of them are opened only these days.
Articles

Live-streaming: how the Chernobyl nuclear power plant was closed

Radioactive contamination: risk factors

COVID-19 and Chernobyl-86: Vaccination for Humanity

Chernobyl toughens up: I don’t strive for social contacts

A new test site in Chernobyl: a nuclear or a garbage one?

Human security: a model of nuclear-free development of mankind

Two pills for fear: on the roof of the 4th power unit of the ChNPP

Myths and truth about Chernobyl: a shot for liquidators
